手写Promise - 实现一个基础的Promise
前端开发中常常会用到Promise,不过有部分人并不清楚Promise的原理,本文也是本人在学习Promise时对Promis的一些认识,但愿能对各位童鞋有所帮助。javascript
手写Promise - 实现一个基础的Promise
[手写Promise - 实例方法catch、finally]()
[手写Promise - 经常使用静态方法all、any、resolve、reject、race]()前端
从认识Promise开始。。。
/* 模拟一个简单的异步行为 */
function fetchData() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('willem');
}, 1000);
});
}
fetchData().then((data) => {
// after 1000ms
console.log(data); // willem
return 'wei';
}, (err) => {}).then((data2) => {
console.log(data2); // wei
});
上面的例子算是一个最多见的用法,可能在使用的时候更多的使用的是catch来处理异常来替代then方法的第二个参数,但catch也只是一个then的语法糖。java
从中咱们能够用一些句子来描述Promise。git
- promise是一个类,它的构造函数接受一个函数,函数的两个参数也都是函数
- 在传入的函数中执行resolve表示成功,执行reject表示失败,传入的值会传给then方法的回调函数
- promise有一个叫作then的方法,该方法有两个参数,第一个参数是成功以后执行的回调函数,第二个参数是失败以后执行的回调函数。then方法在resolve或者reject执行以后才会执行,而且then方法中的值是传给resolve或reject的参数
- promise支持链式调用
有了相应的描述,接下来就是来一步一步实现了。github
简单版Promise
1. promise是一个类,它的构造函数接受一个函数,函数的两个参数也都是函数segmentfault
第一点比较简单数组
// 这里没有使用Promise做为类名是为了方便测试
class WPromise {
constructor(executor) {
// 这里绑定this是为了防止执行时this的指向改变,this的指向问题,这里不过多赘述
executor(this._resolve.bind(this), this._reject.bind(this));
}
_resolve() {}
_reject() {}
}
2. 在传入的函数中执行resolve表示成功,执行reject表示失败,传入的值会传给then方法的回调函数promise
成功、失败,这个很容易想到使用一个状态进行标记,实际上Promise就是这样作的。在Promise中使用了pending、fulfilled、rejected来标识当前的状态。异步
-
pending初始状态,既不是成功,也不是失败状态。等待resolve或者reject调用更新状态。 -
fulfilled意味着操做成功完成。 -
rejected意味着操做失败。
须要注意的一点是,这三个状态之间只存在两个变换关系:函数
-
pending转换为fulfilled,只能由resolve方法完成转换 -
pending转换为rejected,只能由reject方法完成转换
传入的值会传给then的回调函数,怎么传递呢?显然咱们将对resolve和reject的值作一个保存。
将上面的状态和值添加到Promise
class WPromise {
static pending = 'pending';
static fulfilled = 'fulfilled';
static rejected = 'rejected';
constructor(executor) {
executor(this._resolve.bind(this), this._reject.bind(this));
this.status = WPromise.pending; // 初始化状态为pending
this.value = undefined; // 存储 this._resolve 即操做成功 返回的值
this.reason = undefined; // 存储 this._reject 即操做失败 返回的值
}
_resolve(value) {
this.value = value;
this.status = WPromise.fulfilled; // 将状态设置为成功
}
_reject(reason) {
this.reason = reason;
this.status = WPromise.rejected; // 将状态设置为失败
}
}
3. Promise有一个叫作then的方法,该方法有两个参数,第一个参数是成功以后执行的回调函数,第二个参数是失败以后执行的回调函数。then方法在resolve或者reject执行以后才会执行,而且then方法中的值是传给resolve或reject的参数
这句话有点长,须要注意的是这句then方法在resolve或者reject执行以后才会执行,咱们知道Promise是异步的,也就是说then传入的函数是不能立马执行,须要存储起来,在resolve函数执行以后才拿出来执行。
换句话说,这个过程有点相似于发布订阅者模式:咱们使用then来注册事件,那何时来通知这些事件是否执行呢?答案就是在resolve方法执行或者reject方法执行时。
ok, 继续完善咱们的代码。
class WPromise {
static pending = "pending";
static fulfilled = "fulfilled";
static rejected = "rejected";
constructor(executor) {
executor(this._resolve.bind(this), this._reject.bind(this));
this.status = WPromise.pending; // 初始化状态为pending
this.value = undefined; // 存储 this._resolve 即操做成功 返回的值
this.reason = undefined; // 存储 this._reject 即操做失败 返回的值
// 存储then中传入的参数
// 至于为何是数组呢?由于同一个Promise的then方法能够调用屡次
this.callbacks = [];
}
// onFulfilled 是成功时执行的函数
// onRejected 是失败时执行的函数
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 这里能够理解为在注册事件
// 也就是将须要执行的回调函数存储起来
this.callbacks.push({
onFulfilled,
onRejected,
});
}
_resolve(value) {
this.value = value;
this.status = WPromise.fulfilled; // 将状态设置为成功
// 通知事件执行
this.callbacks.forEach((cb) => this._handler(cb));
}
_reject(reason) {
this.reason = reason;
this.status = WPromise.rejected; // 将状态设置为失败
this.callbacks.forEach((cb) => this._handler(cb));
}
_handler(callback) {
const { onFulfilled, onRejected } = callback;
if (this.status === WPromise.fulfilled && onFulfilled) {
// 传入存储的值
onFulfilled(this.value);
}
if (this.status === WPromise.rejected && onRejected) {
// 传入存储的错误信息
onRejected(this.reason);
}
}
}
这个时候的Promise已经渐具雏形,如今能够来简单测试一下
function fetchData(success) {
return new WPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if (success) {
resolve("willem");
} else {
reject('error');
}
}, 1000);
});
}
fetchData(true).then(data => {
console.log(data); // after 1000ms: willem
});
fetchData(false).then(null, (reason) => {
console.log(reason); // after 1000ms: error
});
从上面的输出结果来看,暂时是没什么问题的。接下来就是须要重点关注的链式调用问题了。
重难点:链式调用
链式调用 不知道大家看见这个想到了啥,我反正是想到了jQuery。其实链式调用无非就是再返回一个类的实例,那首先想到的确定就是直接返回this,不过反正自身真的能够吗?
咱们不妨在then方法最后添加一行 return this;来进行一个测试
function fetchData() {
return new WPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('willem');
}, 1000);
});
}
const p1 = fetchData().then(data1 => {return data1 + ' wei'});
const p2 = p1.then((data2) => {console.log(data2);}); // willem 正确输出应该是 'willem wei'
const p3 = p1.then((data3) => {console.log(data3);}); // willem 正确输出应该是 'willem wei'
显然,直接返回this是确定不对,确定要对函数的返回值作一个处理。
这时候可能会有同窗说了,那我处理不就完事了么,我把then回调函数的执行结果赋值给value不就完事。答案固然是否认的,这回引起Promise内部的value和callbacks混乱。
那么,咱们采起的固然是另外一个方案,每次then方法都将返回一个新的Promise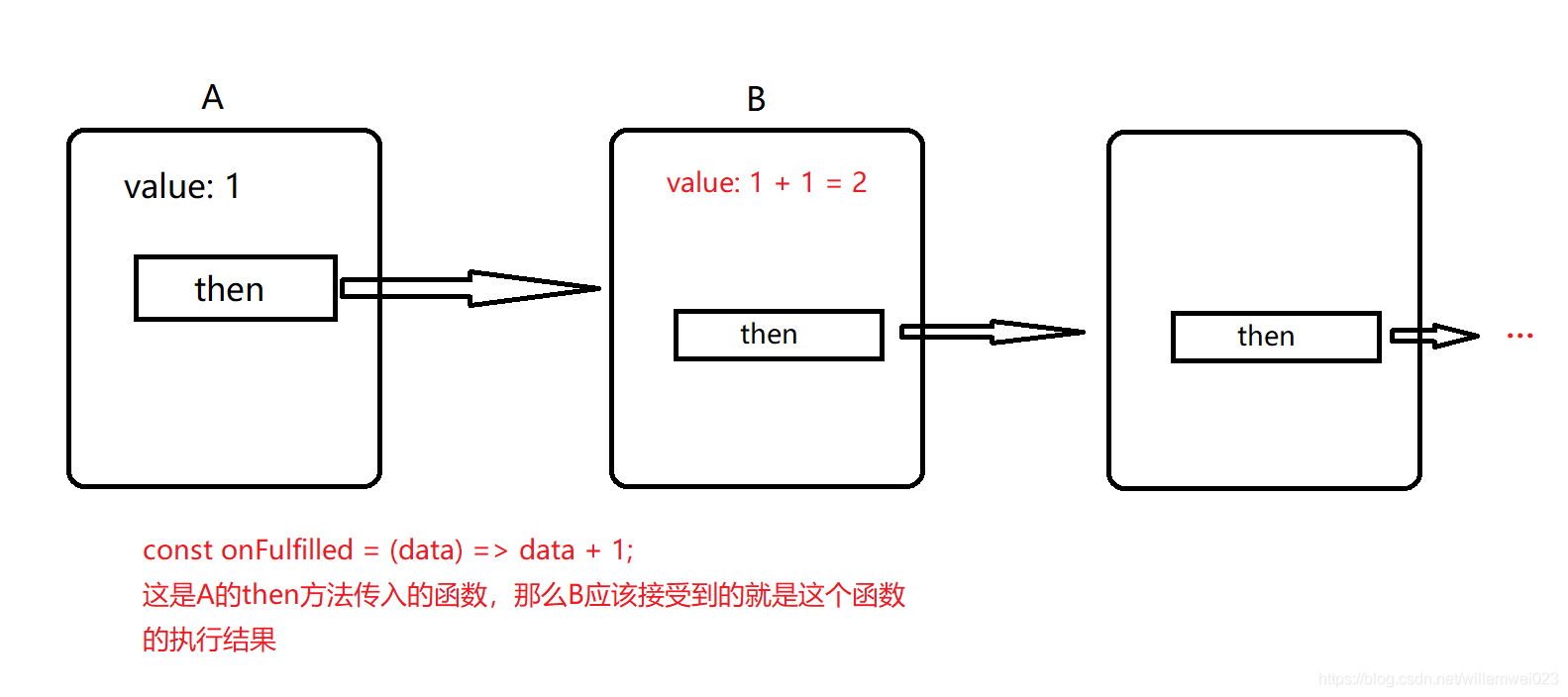
这是一个简单的then的数据走向。简单说一下,then函数中返回的Promise的value值来源于当前then函数的onFulfilled函数(第一个参数)的执行结果(为方便理解,暂时只讨论操做成功的状况)。
从咱们写的代码来看,value值只会在resolve函数中被赋值,显然咱们也将会把onFulfilled执行的结果经过resolve的执行来传入到下一个Promise中。
加入链式调用的处理:
class WPromise {
static pending = "pending";
static fulfilled = "fulfilled";
static rejected = "rejected";
constructor(executor) {
executor(this._resolve.bind(this), this._reject.bind(this));
this.status = WPromise.pending; // 初始化状态为pending
this.value = undefined; // 存储 this._resolve 即操做成功 返回的值
this.reason = undefined; // 存储 this._reject 即操做失败 返回的值
// 存储then中传入的参数
// 至于为何是数组呢?由于同一个Promise的then方法能够调用屡次
this.callbacks = [];
}
// onFulfilled 是成功时执行的函数
// onRejected 是失败时执行的函数
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 返回一个新的Promise
return new WPromise((nextResolve, nextReject) => {
// 这里之因此把下一个Promsie的resolve函数和reject函数也存在callback中
// 是为了将onFulfilled的执行结果经过nextResolve传入到下一个Promise做为它的value值
this.callbacks.push({
nextResolve,
nextReject,
onFulfilled,
onRejected
});
});
}
_resolve(value) {
this.value = value;
this.status = WPromise.fulfilled; // 将状态设置为成功
// 通知事件执行
this.callbacks.forEach((cb) => this._handler(cb));
}
_reject(reason) {
this.reason = reason;
this.status = WPromise.rejected; // 将状态设置为失败
this.callbacks.forEach((cb) => this._handler(cb));
}
_handler(callback) {
const { onFulfilled, onRejected, nextResolve, nextReject } = callback;
if (this.status === WPromise.fulfilled) {
// 传入存储的值
// 未传入onFulfilled时,将undefined传入
const nextValue = onFulfilled ? onFulfilled(this.value) : undefined;
nextResolve(nextValue);
return;
}
if (this.status === WPromise.rejected) {
// 传入存储的错误信息
// 一样的处理
const nextReason = onRejected ? onRejected(this.value) : undefined;
nextReject(nextReason);
}
}
}
咱们再把刚开始的例子拿来测试一下
function fetchData() {
return new WPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('willem');
}, 1000);
});
}
fetchData().then((data) => {
// after 1000ms
console.log(data); // willem
return 'wei';
}, (err) => {}).then((data2) => {
console.log(data2); // wei
});
哟西,没啥问题。不过上面的版本还有个问题没有处理,当onFulfilled执行的结果不是一个简单的值,而就是一个Promise时,后续的then会等待其执行完成以后才执行。
Promise基础版的最终版:
class WPromise {
static pending = "pending";
static fulfilled = "fulfilled";
static rejected = "rejected";
constructor(executor) {
executor(this._resolve.bind(this), this._reject.bind(this));
this.status = WPromise.pending; // 初始化状态为pending
this.value = undefined; // 存储 this._resolve 即操做成功 返回的值
this.reason = undefined; // 存储 this._reject 即操做失败 返回的值
// 存储then中传入的参数
// 至于为何是数组呢?由于同一个Promise的then方法能够调用屡次
this.callbacks = [];
}
// onFulfilled 是成功时执行的函数
// onRejected 是失败时执行的函数
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 返回一个新的Promise
return new WPromise((nextResolve, nextReject) => {
// 这里之因此把下一个Promsie的resolve函数和reject函数也存在callback中
// 是为了将onFulfilled的执行结果经过nextResolve传入到下一个Promise做为它的value值
this.callbacks.push({
nextResolve,
nextReject,
onFulfilled,
onRejected
});
});
}
_resolve(value) {
// 处理onFulfilled执行结果是一个Promise时的状况
// 这里可能理解起来有点困难
// 当value instanof WPromise时,说明当前Promise确定不会是第一个Promise
// 而是后续then方法返回的Promise(第二个Promise)
// 咱们要获取的是value中的value值(有点绕,value是个promise时,那么内部存有个value的变量)
// 怎样将value的value值获取到呢,能够将传递一个函数做为value.then的onFulfilled参数
// 那么在value的内部则会执行这个函数,咱们只须要将当前Promise的value值赋值为value的value便可
if (value instanceof WPromise) {
value.then(this._resolve.bind(this), this._reject.bind(this));
return;
}
this.value = value;
this.status = WPromise.fulfilled; // 将状态设置为成功
// 通知事件执行
this.callbacks.forEach((cb) => this._handler(cb));
}
_reject(reason) {
this.reason = reason;
this.status = WPromise.rejected; // 将状态设置为失败
this.callbacks.forEach((cb) => this._handler(cb));
}
_handler(callback) {
const { onFulfilled, onRejected, nextResolve, nextReject } = callback;
if (this.status === WPromise.fulfilled) {
// 传入存储的值
// 未传入onFulfilled时,将undefined传入
const nextValue = onFulfilled ? onFulfilled(this.value) : undefined;
nextResolve(nextValue);
return;
}
if (this.status === WPromise.rejected) {
// 传入存储的错误信息
// 一样的处理
const nextReason = onRejected ? onRejected(this.value) : undefined;
nextReject(nextReason);
}
}
}
ok,测试一下
function fetchData() {
return new WPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('willem');
}, 1000);
});
}
fetchData().then((data) => {
return new WPromise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(data + ' wei');
}, 1000);
});
}, (err) => {}).then((data2) => {
console.log(data2); // willem wei
});
至此,一个简单的Promise就完成了,固然还有不少须要处理,好比异常等等。
下一篇文章咱们一块儿再来学习一下finally和catch的实现。
- 1. 【原】手写一个promise 手把手教你实现一个完整的 Promise
- 2. 手写一个Promise
- 3. 手写一个promise
- 4. 手写实现promise
- 5. 手写实现Promise
- 6. 学习Promise基础及手写Promise
- 7. 请手写代码实现一个promise
- 8. Promise-手写Promise
- 9. 手写基于Promise A+规范的Promise
- 10. es6 --- > 手写一个promise
- 更多相关文章...
- • 现实生活中的 XML - XML 教程
- • Scala 基础语法 - Scala教程
- • ☆基于Java Instrument的Agent实现
- • Kotlin学习(一)基本语法
-
每一个你不满意的现在,都有一个你没有努力的曾经。