SSM (十五) 乐观锁与悲观锁的实际应用
前言
随着互联网的兴起,如今三高(高可用、高性能、高并发)项目是愈来愈流行。java
本次来谈谈高并发。首先假设一个业务场景:数据库中有一条数据,须要获取到当前的值,在当前值的基础上+10,而后再更新回去。
若是此时有两个线程同时并发处理,第一个线程拿到数据是10,+10=20更新回去。第二个线程本来是要在第一个线程的基础上再+20=40,结果因为并发访问取到更新前的数据为10,+20=30。git
这就是典型的存在中间状态,致使数据不正确。来看如下的例子:github
并发所带来的问题
和上文提到的相似,这里有一张price表,表结构以下:redis
CREATE TABLE `price` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
`total` decimal(12,2) DEFAULT '0.00' COMMENT '总值',
`front` decimal(12,2) DEFAULT '0.00' COMMENT '消费前',
`end` decimal(12,2) DEFAULT '0.00' COMMENT '消费后',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1268 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8复制代码
我这里写了一个单测:就一个主线程,循环100次,每次把front的值减去10,再写入一次流水记录,正常状况是写入的每条记录都会每次减去10。sql
/** * 单线程消费 */
@Test
public void singleCounsumerTest1(){
for (int i=0 ;i<100 ;i++){
Price price = priceMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1);
int ron = 10 ;
price.setFront(price.getFront().subtract(new BigDecimal(ron)));
price.setEnd(price.getEnd().add(new BigDecimal(ron)));
price.setTotal(price.getFront().add(price.getEnd()));
priceMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(price) ;
price.setId(null);
priceMapper.insertSelective(price) ;
}
}复制代码
执行结果以下:数据库
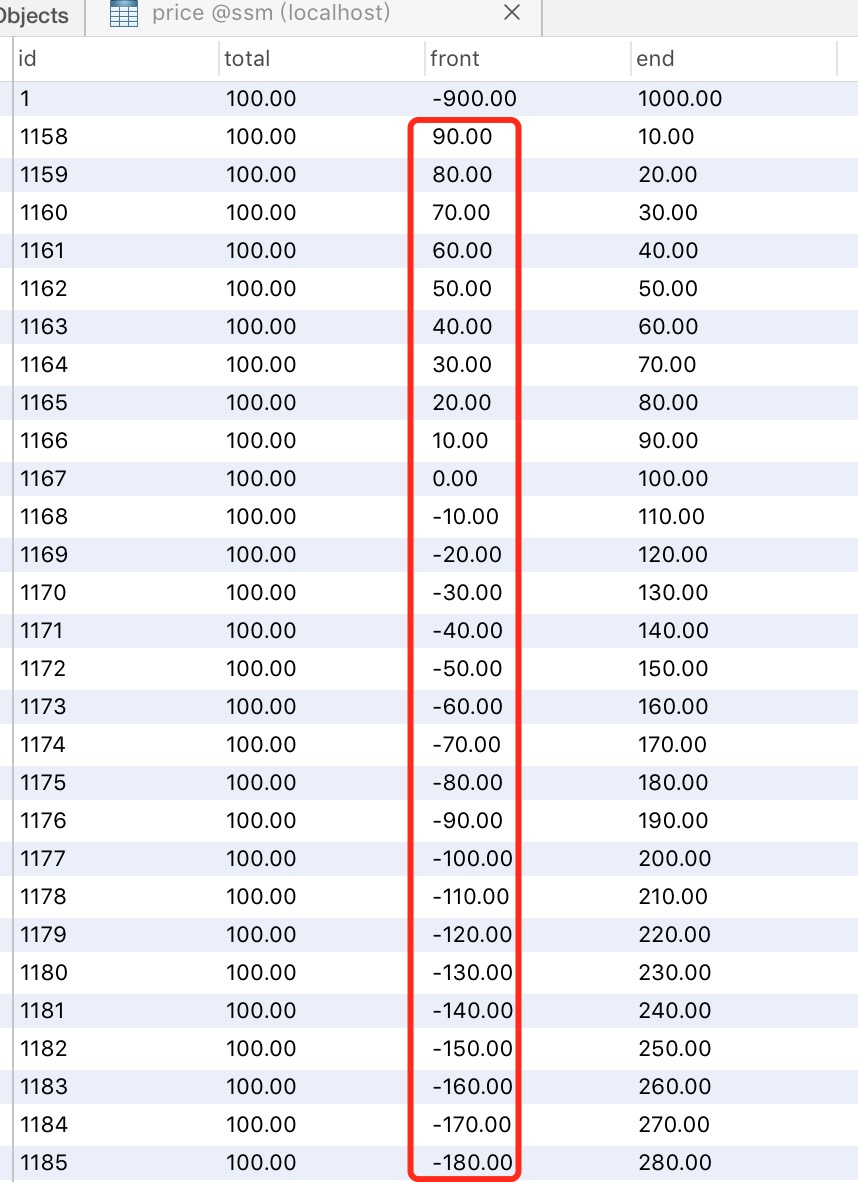
能够看到确实是每次都递减10。
可是若是是多线程的状况下会是如何呢:多线程
我这里新建了一个
PriceController并发
/** * 线程池 无锁 * @param redisContentReq * @return */
@RequestMapping(value = "/threadPrice",method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public BaseResponse<NULLBody> threadPrice(@RequestBody RedisContentReq redisContentReq){
BaseResponse<NULLBody> response = new BaseResponse<NULLBody>() ;
try {
for (int i=0 ;i<10 ;i++){
Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Price price = priceMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1);
int ron = 10 ;
price.setFront(price.getFront().subtract(new BigDecimal(ron)));
price.setEnd(price.getEnd().add(new BigDecimal(ron)));
priceMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(price) ;
price.setId(null);
priceMapper.insertSelective(price) ;
}
});
config.submit(t);
}
response.setReqNo(redisContentReq.getReqNo());
response.setCode(StatusEnum.SUCCESS.getCode());
response.setMessage(StatusEnum.SUCCESS.getMessage());
}catch (Exception e){
logger.error("system error",e);
response.setReqNo(response.getReqNo());
response.setCode(StatusEnum.FAIL.getCode());
response.setMessage(StatusEnum.FAIL.getMessage());
}
return response ;
}复制代码
其中为了节省资源使用了一个线程池:app
@Component
public class ThreadPoolConfig {
private static final int MAX_SIZE = 10 ;
private static final int CORE_SIZE = 5;
private static final int SECOND = 1000;
private ThreadPoolExecutor executor ;
public ThreadPoolConfig(){
executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(CORE_SIZE,MAX_SIZE,SECOND, TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()) ;
}
public void submit(Thread thread){
executor.submit(thread) ;
}
}复制代码
关于线程池的使用从此会仔细探讨。这里就简单理解为有10个线程并发去处理上面单线程的逻辑,来看看结果怎么样:dom
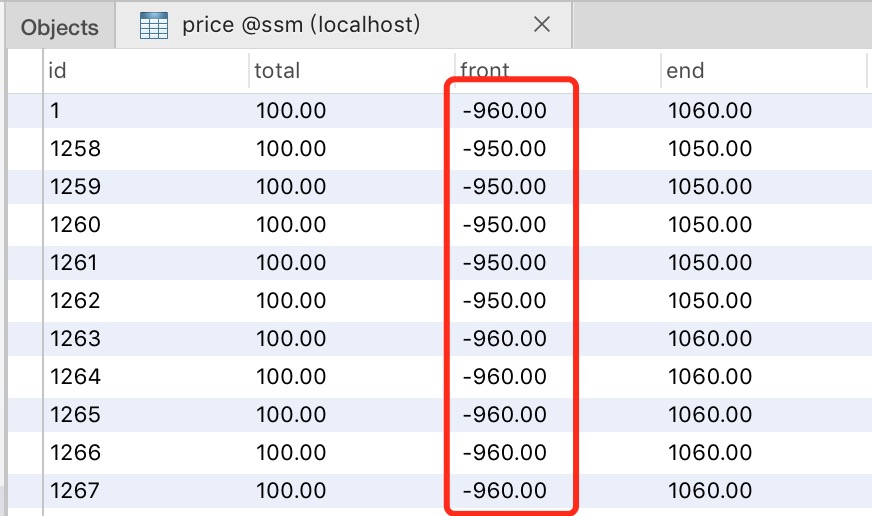
会看到明显的数据错误,致使错误的缘由天然就是有线程读取到了中间状态进行了错误的更新。
进而有了如下两种解决方案:悲观锁和乐观锁。
悲观锁
简单理解下悲观锁:当一个事务锁定了一些数据以后,只有当当前锁提交了事务,释放了锁,其余事务才能得到锁并执行操做。
使用方式以下:
首先要关闭MySQL的自动提交:set autocommit = 0;
bigen --开启事务
select id, total, front, end from price where id=1 for update
insert into price values(?,?,?,?,?)
commit --提交事务复制代码
这里使用select for update的方式利用数据库开启了悲观锁,锁定了id=1的这条数据(注意:这里除非是使用了索引会启用行级锁,否则是会使用表锁,将整张表都锁住。)。以后使用commit提交事务并释放锁,这样下一个线程过来拿到的就是正确的数据。
悲观锁通常是用于并发不是很高,而且不容许脏读等状况。可是对数据库资源消耗较大。
乐观锁
那么有没有性能好,支持的并发也更多的方式呢?
那就是乐观锁。
乐观锁是首先假设数据冲突不多,只有在数据提交修改的时候才进行校验,若是冲突了则不会进行更新。
一般的实现方式增长一个version字段,为每一条数据加上版本。每次更新的时候version+1,而且更新时候带上版本号。实现方式以下:
新建了一张price_version表:
CREATE TABLE `price_version` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
`total` decimal(12,2) DEFAULT '0.00' COMMENT '总值',
`front` decimal(12,2) DEFAULT '0.00' COMMENT '消费前',
`end` decimal(12,2) DEFAULT '0.00' COMMENT '消费后',
`version` int(11) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '并发版本控制',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1268 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8复制代码
更新数据的SQL:
<update id="updateByVersion" parameterType="com.crossoverJie.pojo.PriceVersion">
UPDATE price_version
SET front = #{front,jdbcType=DECIMAL},
version= version + 1
WHERE id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}
AND version = #{version,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</update>复制代码
调用方式:
/** * 线程池,乐观锁 * @param redisContentReq * @return */
@RequestMapping(value = "/threadPriceVersion",method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public BaseResponse<NULLBody> threadPriceVersion(@RequestBody RedisContentReq redisContentReq){
BaseResponse<NULLBody> response = new BaseResponse<NULLBody>() ;
try {
for (int i=0 ;i<3 ;i++){
Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
PriceVersion priceVersion = priceVersionMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1);
int ron = new Random().nextInt(20);
logger.info("本次消费="+ron);
priceVersion.setFront(new BigDecimal(ron));
int count = priceVersionMapper.updateByVersion(priceVersion);
if (count == 0){
logger.error("更新失败");
}else {
logger.info("更新成功");
}
}
});
config.submit(t);
}
response.setReqNo(redisContentReq.getReqNo());
response.setCode(StatusEnum.SUCCESS.getCode());
response.setMessage(StatusEnum.SUCCESS.getMessage());
}catch (Exception e){
logger.error("system error",e);
response.setReqNo(response.getReqNo());
response.setCode(StatusEnum.FAIL.getCode());
response.setMessage(StatusEnum.FAIL.getMessage());
}
return response ;
}复制代码
处理逻辑:开了三个线程生成了20之内的随机数更新到front字段。
当调用该接口时日志以下:
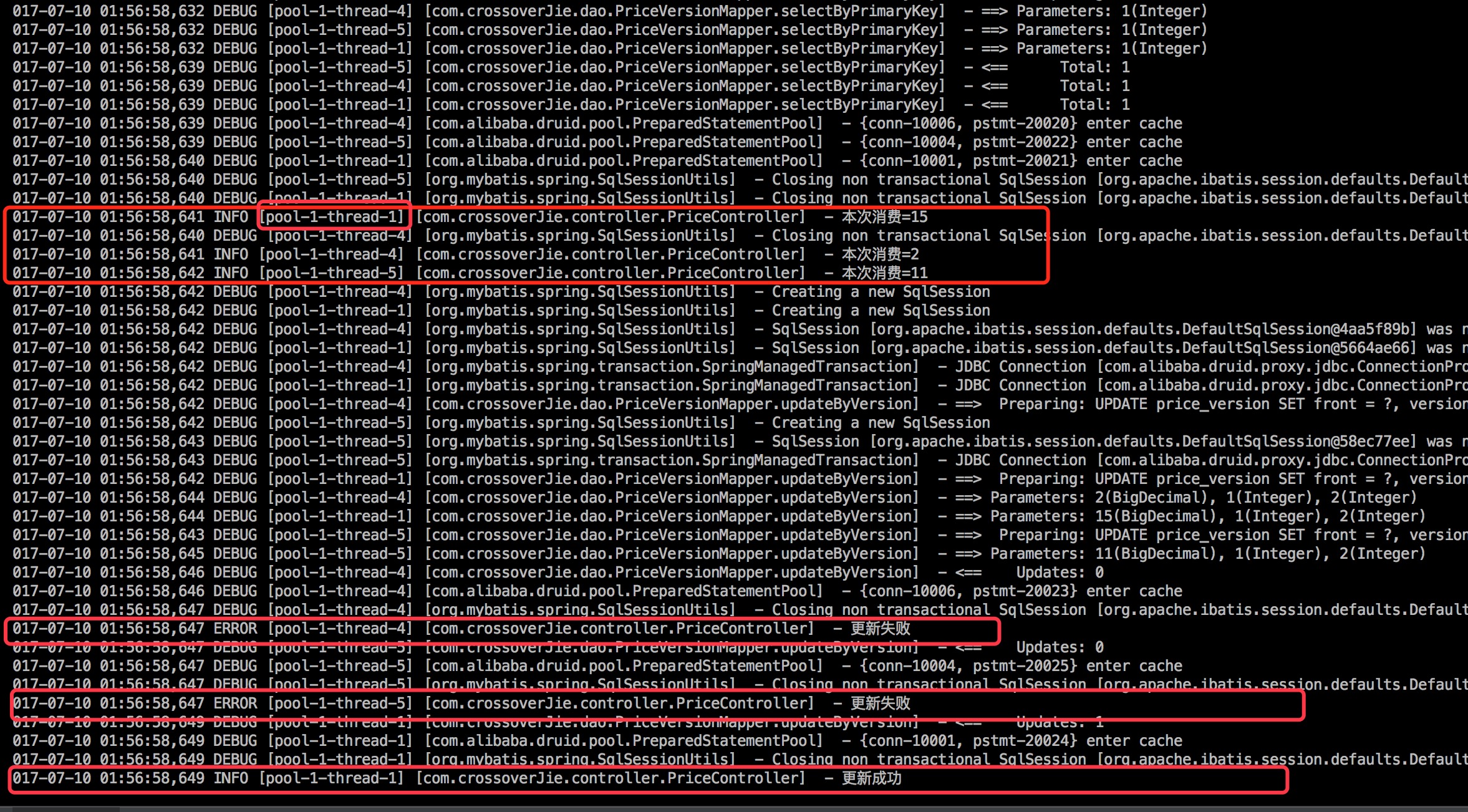
能够看到线程一、四、5分别生成了15,2,11三个随机数。最后线程四、5都更新失败了,只有线程1更新成功了。
查看数据库:

发现也确实是更新的15。
乐观锁在实际应用相对较多,它能够提供更好的并发访问,而且数据库开销较少,可是有可能存在脏读的状况。
总结
以上两种各有优劣,你们能够根据具体的业务场景来判断具体使用哪一种方式来保证数据的一致性。
我的博客地址:crossoverjie.top。

- 1. 关于乐观锁与悲观锁的实际应用
- 2. 乐观锁与悲观锁的实际应用
- 3. 乐观锁与悲观锁
- 4. 悲观锁与乐观锁
- 5. 悲观锁与乐观锁(CAS实现)
- 6. 乐观锁&悲观锁
- 7. hibernate 乐观锁与悲观锁使用
- 8. MySQL锁(4):乐观锁与悲观锁
- 9. MySQL锁-乐观锁与悲观锁
- 更多相关文章...
- • Hibernate悲观锁 - Hibernate教程
- • Hibernate乐观锁 - Hibernate教程
- • 漫谈MySQL的锁机制
- • TiDB 在摩拜单车在线数据业务的应用和实践
-
每一个你不满意的现在,都有一个你没有努力的曾经。
- 1. 关于乐观锁与悲观锁的实际应用
- 2. 乐观锁与悲观锁的实际应用
- 3. 乐观锁与悲观锁
- 4. 悲观锁与乐观锁
- 5. 悲观锁与乐观锁(CAS实现)
- 6. 乐观锁&悲观锁
- 7. hibernate 乐观锁与悲观锁使用
- 8. MySQL锁(4):乐观锁与悲观锁
- 9. MySQL锁-乐观锁与悲观锁