24. Swap Nodes in Pairs[M]两两交换链表中的节点
题目
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head.
You may not modify the values in the list's nodes, only nodes itself may be changed.
Example:
Given 1->2->3->4,you should return the list as 2->1->4->3.node
思路
思路一:遍历交换
本题须要咱们对链表进行两两的交换,而且
1.如何交换表头
这里已经用过不少遍了,在链表的表头增长一个辅助节点。python
ListNode* result = new ListNode(-1); result->next = head;
2.如何进行链表的两两交换
链表的交换涉及到三个节点:当前节点(cur),当前节点的下一个节点(first),当前节点的下下个节点(second),交换原理如图1:.net
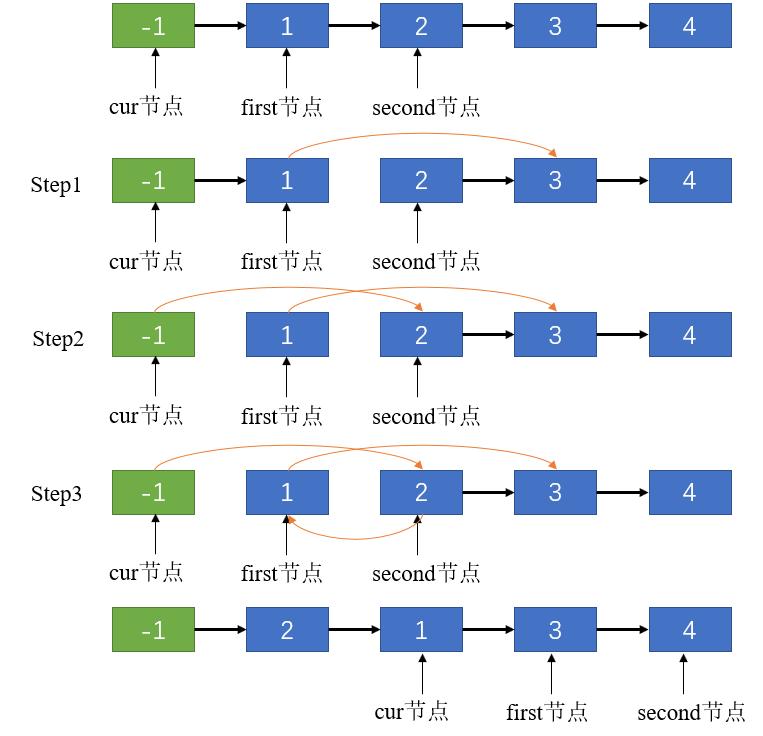
- 思路一
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr || nullptr)
return head;
ListNode* result = new ListNode(0);
result->next = head;
ListNode* cur = result;
while(cur->next != nullptr && cur->next->next != nullptr){
ListNode* first = cur->next;
ListNode* second = cur->next->next;
//节点交换
first->next = second->next;
cur->next = second;
cur->next->next = first;
cur = cur->next->next;
}
return result->next;
}
};
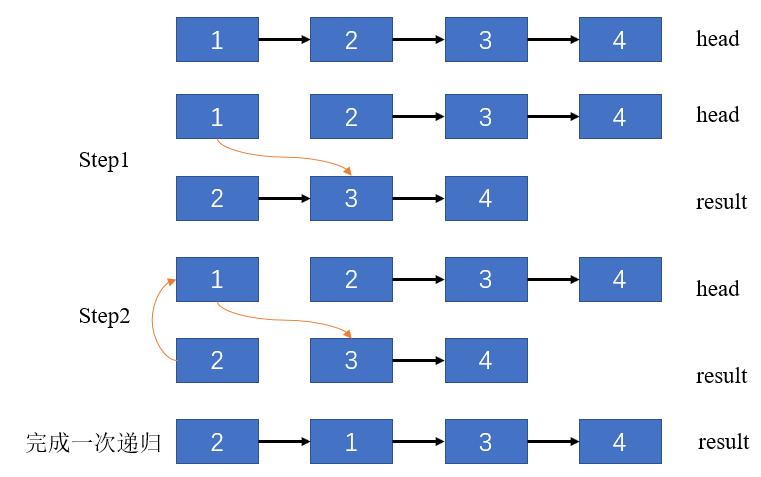
- 思路二
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return head;
ListNode* result = head -> next;
head->next = swapPairs(result->next);
result->next = head;
return result;
}
};
Python
参考
相关文章
- 1. [Swift]LeetCode24. 两两交换链表中的节点 | Swap Nodes in Pairs
- 2. [LeetCode_24] Swap Nodes in Pairs_两两交换链表中的节点
- 3. [LeetCode] 24. Swap Nodes in Pairs ☆☆☆(链表,相邻两节点交换)
- 4. LeetCode 24. Swap Nodes in Pairs | 交换两个node(链表)
- 5. LeetCode 第 24 号问题:两两交换链表中的节点
- 6. 24. 两两交换链表中的节点
- 7. leetcode #24 两两交换链表中的节点(C++)递归
- 8. 24. Swap Nodes in Pairs(成对交换链表节点)Python
- 9. 画解算法:24. 两两交换链表中的节点
- 10. Leetcode 24 两两交换链表中的节点【链表】
- 更多相关文章...
- • XML DOM 替换节点 - XML DOM 教程
- • XML DOM 节点列表 - XML DOM 教程
- • C# 中 foreach 遍历的用法
- • Scala 中文乱码解决
相关标签/搜索
每日一句
-
每一个你不满意的现在,都有一个你没有努力的曾经。
最新文章
- 1. Duang!超快Wi-Fi来袭
- 2. 机器学习-补充03 神经网络之**函数(Activation Function)
- 3. git上开源maven项目部署 多module maven项目(多module maven+redis+tomcat+mysql)后台部署流程学习记录
- 4. ecliple-tomcat部署maven项目方式之一
- 5. eclipse新导入的项目经常可以看到“XX cannot be resolved to a type”的报错信息
- 6. Spark RDD的依赖于DAG的工作原理
- 7. VMware安装CentOS-8教程详解
- 8. YDOOK:Java 项目 Spring 项目导入基本四大 jar 包 导入依赖,怎样在 IDEA 的项目结构中导入 jar 包 导入依赖
- 9. 简单方法使得putty(windows10上)可以免密登录树莓派
- 10. idea怎么用本地maven
欢迎关注本站公众号,获取更多信息

相关文章
- 1. [Swift]LeetCode24. 两两交换链表中的节点 | Swap Nodes in Pairs
- 2. [LeetCode_24] Swap Nodes in Pairs_两两交换链表中的节点
- 3. [LeetCode] 24. Swap Nodes in Pairs ☆☆☆(链表,相邻两节点交换)
- 4. LeetCode 24. Swap Nodes in Pairs | 交换两个node(链表)
- 5. LeetCode 第 24 号问题:两两交换链表中的节点
- 6. 24. 两两交换链表中的节点
- 7. leetcode #24 两两交换链表中的节点(C++)递归
- 8. 24. Swap Nodes in Pairs(成对交换链表节点)Python
- 9. 画解算法:24. 两两交换链表中的节点
- 10. Leetcode 24 两两交换链表中的节点【链表】